H13 Tool Steel Hardness: Methods to Test and Optimize Performance
Introduction
H13 tool steel stands out for its remarkable durability and thermal resistance, making it a preferred choice in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. However, its effectiveness hinges on maintaining optimal hardness, which directly impacts wear resistance, toughness, and performance under stress. This article explores various methods for testing H13 steel hardness and strategies to optimize it for maximum utility.

What is H13 Tool Steel?
H13 is a chromium-molybdenum hot work tool steel renowned for its exceptional strength and heat resistance. It contains:
- Chromium for enhanced corrosion resistance.
- Molybdenum and vanadium for superior toughness and wear resistance.
H13’s properties make it ideal for applications like:
- Forging dies.
- Injection molding tools.
- Extrusion dies.
- Die-casting components.
This robust tool steel withstands thermal fatigue, making it invaluable in environments with rapid temperature fluctuations.
Understanding Hardness in Tool Steel
Hardness measures a material’s resistance to deformation or penetration, a critical factor for tools subjected to high pressures or temperatures. For H13 tool steel:
- High hardness ensures excellent wear resistance, extending the tool’s lifespan.
- Optimal hardness improves impact resistance while maintaining necessary toughness.
Balancing hardness with toughness is essential; overly hard tools risk brittleness, reducing functionality.
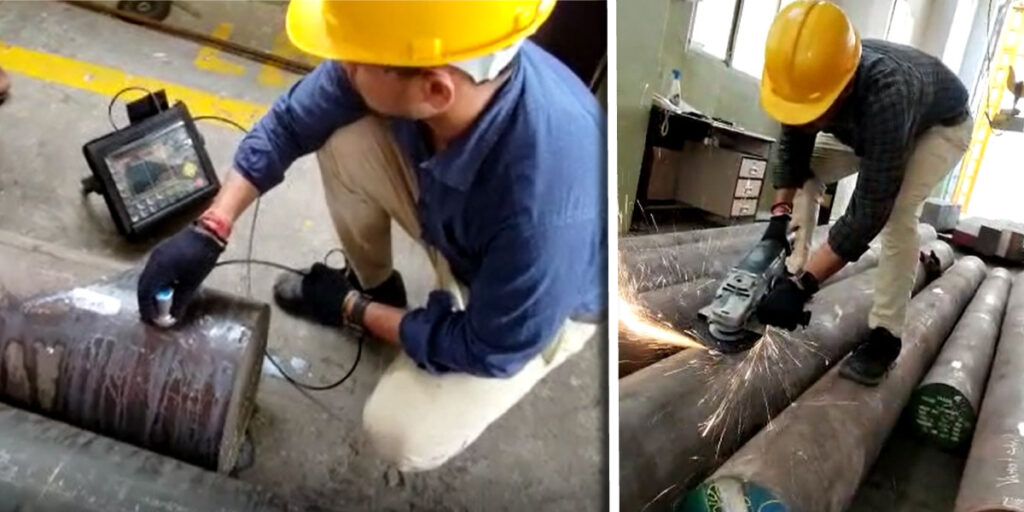
Methods to Test H13 Tool Steel Hardness
1. Rockwell Hardness Test
The Rockwell Hardness Test (HRC scale) is widely used for metals. Here’s how it works:
- Process: A steel or diamond cone presses into the metal at a specific force.
- Outcome: The depth of the indentation determines the hardness.
For H13, the HRC scale typically indicates a hardness range of 40-55 HRC, depending on the heat treatment.
2. Brinell Hardness Test
The Brinell method calculates hardness by indenting the material with a steel ball under a fixed load.
- Suitable for measuring bulk hardness of H13.
- Offers consistent readings for thicker or unevenly treated samples.
3. Vickers Hardness Test
Known for its accuracy, the Vickers method uses a diamond-shaped indenter and microscopic measurements.
- Ideal for smaller H13 components or thin sections.
- Useful for quality control in tool production.
4. Knoop Hardness Test
The Knoop test is used for micro-hardness analysis, measuring the steel’s resistance on a finer scale.
- Best for analyzing surface treatments and coatings.
Factors Affecting the Hardness of H13 Tool Steel
1. Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is the primary determinant of H13 steel hardness. Quenching, followed by tempering, defines its final mechanical properties.
2. Tempering Process
Tempering adjusts the steel’s toughness after hardening. Improper tempering can lower hardness, compromising performance.
3. Alloy Composition
Elements like chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium significantly influence the steel’s ability to retain hardness over time.
Optimizing Performance of H13 Tool Steel
1. Controlled Heat Treatment
Controlled heating and cooling cycles during manufacturing are crucial for achieving precise hardness levels. Recommended approach:
- Preheat at 400-600°C.
- Harden by heating to 1000-1050°C, followed by oil quenching.
2. Cryogenic Processing
This advanced method involves cooling H13 steel to sub-zero temperatures (-196°C).
- Benefits:
- Reduces retained austenite.
- Enhances hardness and wear resistance.
Cryogenic treatment has shown to extend H13’s operational life by 200-300%.
3. Surface Coatings
Adding protective coatings like nitriding or PVD improves both hardness and corrosion resistance. These coatings form a hardened outer layer, shielding the tool from thermal fatigue.
Real-World Applications of Optimized H13 Tool Steel
Industries such as aerospace and automotive rely heavily on H13 tools optimized for hardness. For example:
- Injection molds for plastic benefit from minimized wear and deformation.
- Forging dies withstand high pressures with maintained structural integrity.
Maintenance and Care for Optimal Hardness
Prolonging H13’s hardness involves:
- Regular inspection for signs of wear or fatigue.
- Applying re-coating or re-tempering when necessary.
- Avoiding overheating during operation, which can soften the material.
Conclusion
H13 tool steel, when optimized for hardness, delivers unparalleled performance in demanding applications. By utilizing precise testing methods and implementing techniques like heat treatment and cryogenic processing, industries can maximize the lifespan and utility of this versatile material.
FAQs
- What is the ideal hardness range for H13 tool steel?
The recommended hardness range is 40-55 HRC, depending on the specific application. - Can the hardness of H13 tool steel be restored after wear?
Yes, re-tempering and surface treatments can rejuvenate its hardness. - How does hardness testing benefit tool steel applications?
Testing ensures tools meet application-specific requirements, enhancing performance and durability. - What makes cryogenic processing effective for H13 steel?
It reduces retained austenite, increasing hardness and extending lifespan. - Is there a difference in hardness testing methods for thin and thick sections?
Yes, methods like Vickers or Knoop are suitable for thinner sections, while Brinell or Rockwell are ideal for bulk testing.
Virat Special Steels: A Leader in H13 Steel Supplies
Virat Special Steels is a renowned name in delivering high-quality tool steels, including H13. With decades of industry expertise, Virat has built a reputation for reliability and superior service. Industries across automotive, aerospace, and plastic molding trust Virat for their steel requirements.
Virat Special Steels is the largest Supplier & Stockiest of H13 Steel in India. Consult our team who will assist you for H-13/ DIN 2344 / AISI H13 steel query. https://www.viratsteels.com/h13.html
Size Range in Forged / Rolled Bars:
Rounds: 13mm Dia to 1500mm Dia
Rectangular: Thickness 13mm – 500mm / Width 13mm to 1500mm
For more information or to discuss your steel needs, Virat Special Steels invites you to reach out through their contact details provided, ensuring a professional and informative experience.
Any further queries feel free to contact us :
🌐https://www.viratsteel.in 📬 info@viratsteels.com ☎+91 98140-21775